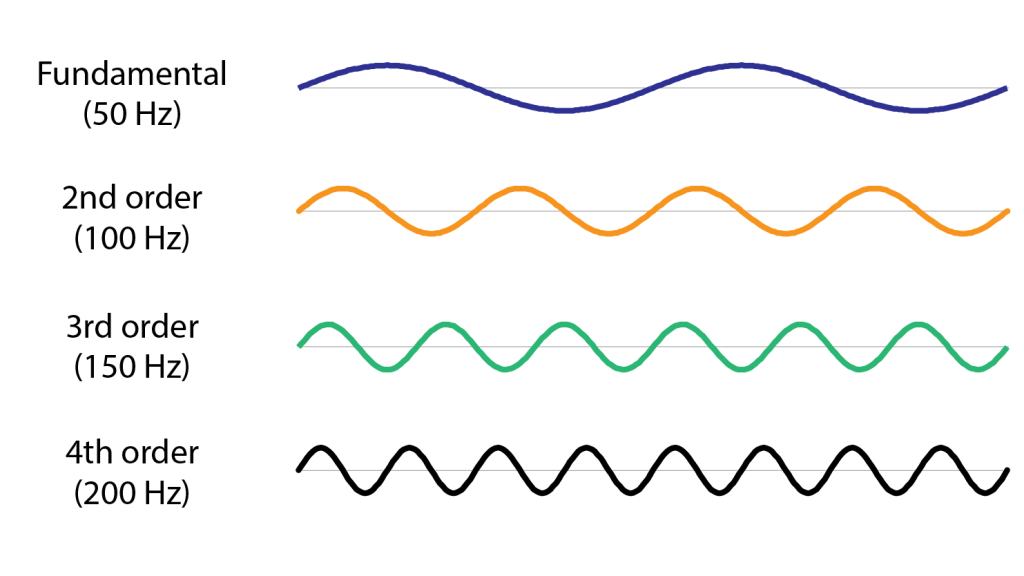
What is harmonic distortion and what does the THD value mean?
Harmonic distortion is a phenomenon in which unwanted frequency components are generated in an electrical or acoustic signal. These additional frequencies are integer multiples of the fundamental frequency of the original signal and can cause an unwanted alteration in the waveform.
When a signal is distorted harmonically, its waveform is altered in some way. In the case of electrical signals, such as those found in audio systems, electric musical instruments, recording equipment, etc., this distortion can be caused by various reasons, such as poorly adjusted amplifiers, overloads in the system, electromagnetic interference, among others.
In the case of electrical signals, such as those found in audio systems, electric musical instruments, recording equipment, etc., this distortion can be caused by various reasons, such as poorly adjusted amplifiers, system overloads, electromagnetic interference, among others.
In the case of acoustic signals, such as those produced by musical instruments or vocals, harmonic distortion can occur due to saturation of the components of a recording or playback system, poorly designed loudspeakers, among other factors.
Harmonic distortion can be undesirable in many situations, especially when faithful and accurate reproduction of the original sound is sought, such as in music, and voice recordings. However, in some musical applications, such as electric guitar, players may deliberately seek this effect in order to obtain certain characteristic tones or timbres.
In any case, for most audio applications, the aim is to minimise harmonic distortion in order to preserve the quality and fidelity of the original signal.
What is the THD of music equipment?
The THD or total harmonic distortion is found in the technical specifications of the equipment. It is assumed that the lower the THD value, the better it sounds.
However, some harmonics from distortion are easier to tolerate than others, and can even make the sound more attractive and warmer. This is the case with the distortion of the even harmonics of tube amplifiers.
To avoid harmonic distortion in audio equipment, especially in hi-fi systems and in environments where accurate sound reproduction is desired, here are some steps you can take:
1. Selecting quality equipment:
- Opt for high-quality, name-brand audio equipment. Lower quality components tend to generate more harmonic distortion.
2. Equipment power and capacity:
- Make sure your amplifier's output power is adequate for your speakers. An amplifier that falls short can distort when trying to produce a louder volume than it can handle.
3. Proper system setup:
- Adjust the gain and volume levels in your system properly. Avoid very high levels that can cause overload and distortion in the amplifiers.
4. Use quality cables:
- Use quality audio cables and avoid cables that are too long, as they can introduce interference and increase distortion.
5. Good isolation and power distribution:
- Make sure your equipment is connected to stable, interference-free power supplies. Power conditioners can help in environments with electrical problems.
6. Avoid input overload:
- When connecting external devices (such as music players, phones, etc.), make sure that the input signals are not too high, which could cause distortion in the preamplifier.
7. Use of filters and attenuators:
- In some cases, especially in high-end systems, harmonic filters and attenuators may be used to eliminate or reduce harmonic distortion.
8. Regular maintenance:
- Periodically maintain your equipment, such as cleaning connectors, checking cables and components, to ensure that they are working optimally.
9. Avoid overuse:
- Avoid continuous use of your equipment at extremely high levels for extended periods of time, as this can cause component fatigue and increase the likelihood of distortion.
10. Equalisation and configuration adjustments:
- Make careful adjustments to the equalisation and configuration of your audio system to get the best performance without overloading any components.
By following these practices, you can help minimise harmonic distortion in your audio equipment and enjoy a more faithful and accurate reproduction of sound.
How is THD (Total Harmonic Distortion) calculated?
THD is the ratio of the total harmonic component to the fundamental component. Specifically, it is expressed by the following calculation formula:
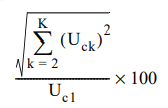
The numerator is the sum of the rms values of each order starting from the second order. The denominator is the rms value of the fundamental waveform.
The denominator is the rms value of the fundamental waveform.
What THD value is advisable in loudspeakers?
The lower the THD, the closer the audio signal in the speakers is to the original sound source, be it an instrument or a wave file. This means that harmonic distortion is often the term for unwanted signal distortion, so audio developers try to keep distortion as low as possible.
In high quality loudspeakers and hi-fi audio systems, THD is sought as low as possible for accurate sound reproduction.
High Fidelity loudspeakers and high quality audio systems:
- For high-fidelity loudspeakers and high-end audio systems, a THD below 1% is generally considered acceptable and offers high-quality sound reproduction.
Studio and monitoring loudspeakers:
- In studio recording and monitoring environments, an even lower THD, often below 0.1% or even less, is preferred for accurate, distortion-free sound reproduction.
General purpose and portable speakers:
- For general purpose speakers, such as computer speakers, Bluetooth speakers, etc., a THD below 5% may be acceptable for decent performance, although lower values will be preferable for better sound quality.
It is important to note that THD is not the only measure of speaker quality. Other factors such as frequency response, sensitivity, impedance, among others, are also important in evaluating the reproduction quality of a loudspeaker.
In high quality loudspeakers and hi-fi audio systems, a THD below 1% is sought after for accurate sound reproduction. However, in general-purpose loudspeakers, values below 5% may be acceptable, although it is always advisable to look for lower values for better sound quality.









